2024-07-16 15:41:58
参考链接:
- 技术选型与调研-流程引擎(工作流引擎–BPM引擎):Activiti、Flowable、Camunda
- 流程引擎架构设计
- 如何设计一个流程引擎
- fixflow中国最好的流程引擎
- 流程引擎比较分析
- compileflow 阿里开源流程引擎
- goflow 规则引擎
- 可视化任务调度系统,精简到一个二进制文件
- rulego IoT规则引擎
- argo-workflows github
- Argo:云原生的工作流引擎
- ArgoWorkflow教程(二)—流水线正确打开方式:Workflow & Template 概念模型
- 蓝鲸SOPS
- 蓝鲸标准流程引擎
- Argo Workflow源码解析源码解析
背景
前言
基础概念
技术调研
设计要点
项目分析(以rulego为例)
rulego简介
RuleGo是一个基于Go语言的轻量级、高性能、嵌入式、可编排组件式的规则引擎。支持异构系统数据集成,可以对输入消息进行聚合、分发、过滤、转换、丰富和执行各种动作。对应编辑页面:统一编辑页面

rulego 功能&架构
核心功能
rulego的核心功能如下
- 程编排: 支持对规则链组件进行动态编排,不重启应用情况下,替换或者新增业务逻辑。
- 扩展简单: 提供丰富灵活的扩展接口,可以很容易地实现自定义组件或者引入第三方组件。
- 动态加载: 支持通过Go plugin 动态加载组件和扩展组件。
- 规则链嵌套: 支持子规则链嵌套,实现流程复用。
- 内置大量组件: 消息类型路由,脚本路由,脚本过滤器,脚本转换器,HTTP推送,MQTT推送,发送邮件,日志记录,数据库操作 等组件。可以自行扩展自定义组件。
- 上下文隔离机制: 可靠的上下文隔离机制,无需担心高并发情况下的数据串流。
- AOP机制: 允许在不修改规则链或节点的原有逻辑的情况下,对规则链的执行添加额外的行为,或者直接替换原规则链或者节点逻辑。
核心架构
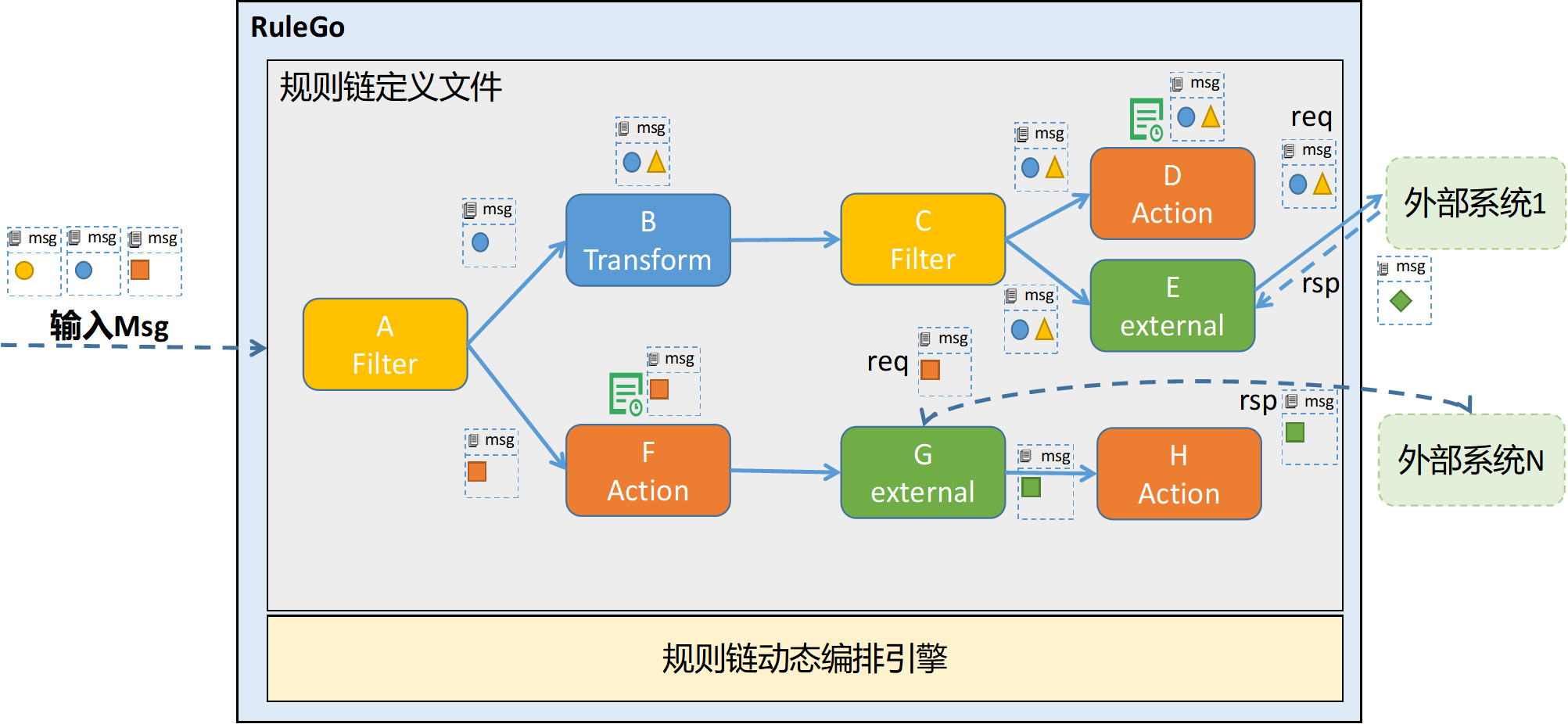
其核心功能还是以任务系统的链式处理自动化为主,实现了自定义切片、组件函数等多种模式。核心架构如下图:

规则链处理消息/事件流程图如下图:
rulego 代码分析
rulego核心在于推理引擎的创建与推理过程两个部分
执行引擎创建
ruluego 解析json字符串完成规则链的初始化定义,同时完成模板上下文的初始化。从examples/call_rest_service/call_rest_service.go为主要入口,梳理函数调用链路如下:
rulego.New(创建新规则引擎) -> newRuleEngine(创建规则引擎对象) -> ruleEngine.ReloadSelf(加载规则配置) -> Parser.DecodeRuleChain(解码types.RuleChain对象) -> InitRuleChainCtx(初始化上下文) -> 完成创建。对应关键代码分析如下:
rulego.New
// 最终调用 engine.Pool.New 进行规则引擎的创建
// https://github.com/CNST-AK47/rulego/blob/ef8fe6762e51b6a509d765226d9fb23cb6b139ae/engine/pool.go#75
// New creates a new RuleEngine instance and stores it in the rule chain pool.
// If the specified id is empty, the ruleChain.id from the rule chain file is used.
func (g *Pool) New(id string, rootRuleChainSrc []byte, opts ...types.RuleEngineOption) (types.RuleEngine, error) {
// Check if an instance with the given ID already exists.
// 直接从引擎中加载
if v, ok := g.entries.Load(id); ok {
return v.(*RuleEngine), nil
} else {
// 新增参数设置
opts = append(opts, types.WithRuleEnginePool(g))
// Create a new rule engine instance.
// 创建一个新实例--
if ruleEngine, err := newRuleEngine(id, rootRuleChainSrc, opts...); err != nil {
return nil, err
} else {
// Store the new rule engine instance in the pool.
// 将实例放到内存池中
if ruleEngine.Id() != "" {
g.entries.Store(ruleEngine.Id(), ruleEngine)
}
return ruleEngine, err
}
}
}
newRuleEngine
// 创建新的规则引擎推理实例
// https://github.com/CNST-AK47/rulego/blob/688f5f254635ab138d9081314bbb977fd3200c97/engine/engine.go
// newRuleEngine creates a new RuleEngine instance with the given ID and definition.
// It applies the provided RuleEngineOptions during the creation process.
// 创建新规则引擎
func newRuleEngine(id string, def []byte, opts ...types.RuleEngineOption) (*RuleEngine, error) {
if len(def) == 0 {
return nil, errors.New("def can not nil")
}
// Create a new RuleEngine with the Id
// 创建对应的规则引擎对象
ruleEngine := &RuleEngine{
id: id,
Config: NewConfig(), // 配置项
ruleChainPool: DefaultPool,
}
// 加载规则引擎配置
err := ruleEngine.ReloadSelf(def, opts...)
if err == nil && ruleEngine.rootRuleChainCtx != nil {
if id != "" {
// 设置规则引擎上下文Id
ruleEngine.rootRuleChainCtx.Id = types.RuleNodeId{Id: id, Type: types.CHAIN}
} else {
// Use the rule chain ID if no ID is provided.
ruleEngine.id = ruleEngine.rootRuleChainCtx.Id.Id
}
}
// Set the aspect lists.
// 设置切面,
startAspects, endAspects, completedAspects := ruleEngine.Aspects.GetChainAspects()
// 设置开始切面
ruleEngine.startAspects = startAspects
// 设置结束切面
ruleEngine.endAspects = endAspects
// 设置环绕切面
ruleEngine.completedAspects = completedAspects
return ruleEngine, err
}
ruleEngine.ReloadSelf(加载规则)
// https://github.com/CNST-AK47/rulego/blob/688f5f254635ab138d9081314bbb977fd3200c97/engine/engine.go
// 执行规则加载
// ReloadSelf 重新加载规则链
func (e *RuleEngine) ReloadSelf(def []byte, opts ...types.RuleEngineOption) error {
// Apply the options to the RuleEngine.
for _, opt := range opts {
_ = opt(e)
}
// 检查是否已经初始化--用于重新加载规则时使用
if e.Initialized() {
//初始化内置切面
if len(e.Aspects) == 0 {
e.initBuiltinsAspects()
}
e.rootRuleChainCtx.config = e.Config
e.rootRuleChainCtx.SetAspects(e.Aspects)
//更新规则链
err := e.rootRuleChainCtx.ReloadSelf(def)
//设置子规则链池
e.rootRuleChainCtx.SetRuleEnginePool(e.ruleChainPool)
return err
} else {
//初始化内置切面
e.initBuiltinsAspects()
//初始化
// 进行规则解析,解析对应的规则结构体
if ctx, err := e.Config.Parser.DecodeRuleChain(e.Config, e.Aspects, def); err == nil {
if e.rootRuleChainCtx != nil {
ctx.(*RuleChainCtx).Id = e.rootRuleChainCtx.Id
}
e.rootRuleChainCtx = ctx.(*RuleChainCtx)
//设置子规则链池
//方便上下文查找更新
e.rootRuleChainCtx.SetRuleEnginePool(e.ruleChainPool)
//执行创建切面逻辑
_, _, createdAspects, _, _ := e.Aspects.GetEngineAspects()
for _, aop := range createdAspects {
// 创建对应的aop点
if err := aop.OnCreated(e.rootRuleChainCtx); err != nil {
return err
}
}
e.initialized = true
return nil
} else {
return err
}
}
}
Parser.DecodeRuleChain
// 进行规则链解析
// https://github.com/CNST-AK47/rulego/blob/688f5f254635ab138d9081314bbb977fd3200c97/engine/parser.go
// 进行基础规则解析
func (p *JsonParser) DecodeRuleChain(config types.Config, aspects types.AspectList, dsl []byte) (types.Node, error) {
// 解析加载types.RuleChain
if rootRuleChainDef, err := ParserRuleChain(dsl); err == nil {
//初始化
// 进行规则引擎初始化
return InitRuleChainCtx(config, aspects, &rootRuleChainDef)
} else {
return nil, err
}
}
// .......
// ParserRuleChain 通过json解析规则链结构体
// 将其解析为rulechain对象
func ParserRuleChain(rootRuleChain []byte) (types.RuleChain, error) {
var def types.RuleChain
err := json.Unmarshal(rootRuleChain, &def)
return def, err
}
InitRuleChainCtx
// 初始化规则引擎上下文
// https://github.com/CNST-AK47/rulego/blob/688f5f254635ab138d9081314bbb977fd3200c97/engine/chain.go
// InitRuleChainCtx initializes a RuleChainCtx with the given configuration, aspects, and rule chain definition.
// 初始化规则链上下文
func InitRuleChainCtx(config types.Config, aspects types.AspectList, ruleChainDef *types.RuleChain) (*RuleChainCtx, error) {
// Retrieve aspects for the engine.
// 获取切面上下文
chainBeforeInitAspects, _, _, afterReloadAspects, destroyAspects := aspects.GetEngineAspects()
// 执行规则引擎初始化函数
for _, aspect := range chainBeforeInitAspects {
// 规则引擎初始化的节点
if err := aspect.OnChainBeforeInit(ruleChainDef); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
// Initialize a new RuleChainCtx with the provided configuration and aspects.
// 初始化规则链上下文
var ruleChainCtx = &RuleChainCtx{
config: config, // 配置信息
SelfDefinition: ruleChainDef, // 规则链定义
nodes: make(map[types.RuleNodeId]types.NodeCtx), // 规则链中节点
nodeRoutes: make(map[types.RuleNodeId][]types.RuleNodeRelation), // 规则链中节点关联列表
relationCache: make(map[RelationCache][]types.NodeCtx), // 对应缓存
componentsRegistry: config.ComponentsRegistry, // 全局组件注册器
initialized: true, // 师傅已经初始化
aspects: aspects, // 切面
afterReloadAspects: afterReloadAspects, // 重载后切片
destroyAspects: destroyAspects, // 销毁切片
}
// Set the ID of the rule chain context if provided in the definition.
if ruleChainDef.RuleChain.ID != "" {
ruleChainCtx.Id = types.RuleNodeId{Id: ruleChainDef.RuleChain.ID, Type: types.CHAIN}
}
// Process the rule chain configuration's vars and secrets.
// 进行规则链中配置上下文的处理
if ruleChainDef != nil && ruleChainDef.RuleChain.Configuration != nil {
// 获取定义配置
varsConfig := ruleChainDef.RuleChain.Configuration[types.Vars]
// 将其转变为map
ruleChainCtx.vars = str.ToStringMapString(varsConfig)
// 获取环境配置
envConfig := ruleChainDef.RuleChain.Configuration[types.Secrets]
// 加密信息
secrets := str.ToStringMapString(envConfig)
// 解密信息
ruleChainCtx.decryptSecrets = decryptSecret(secrets, []byte(config.SecretKey))
}
// 获取节点列表
nodeLen := len(ruleChainDef.Metadata.Nodes)
ruleChainCtx.nodeIds = make([]types.RuleNodeId, nodeLen)
// Load all node information.
// 加载所有节点
for index, item := range ruleChainDef.Metadata.Nodes {
if item.Id == "" {
item.Id = fmt.Sprintf(defaultNodeIdPrefix+"%d", index)
}
ruleNodeId := types.RuleNodeId{Id: item.Id, Type: types.NODE}
ruleChainCtx.nodeIds[index] = ruleNodeId
// 初始化节点上下文
ruleNodeCtx, err := InitRuleNodeCtx(config, ruleChainCtx, aspects, item)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 更新节点上下文
ruleChainCtx.nodes[ruleNodeId] = ruleNodeCtx
}
// Load node relationship information.
// 登记节点之间的关联关系
for _, item := range ruleChainDef.Metadata.Connections {
inNodeId := types.RuleNodeId{Id: item.FromId, Type: types.NODE}
outNodeId := types.RuleNodeId{Id: item.ToId, Type: types.NODE}
ruleNodeRelation := types.RuleNodeRelation{
InId: inNodeId,
OutId: outNodeId,
RelationType: item.Type,
}
// 查询节点关系
nodeRelations, ok := ruleChainCtx.nodeRoutes[inNodeId]
if ok {
nodeRelations = append(nodeRelations, ruleNodeRelation)
} else {
nodeRelations = []types.RuleNodeRelation{ruleNodeRelation}
}
// 更新节点路由
ruleChainCtx.nodeRoutes[inNodeId] = nodeRelations
}
// Load sub-rule chains.
// 加载子规则链关联关系
for _, item := range ruleChainDef.Metadata.RuleChainConnections {
inNodeId := types.RuleNodeId{Id: item.FromId, Type: types.NODE}
outNodeId := types.RuleNodeId{Id: item.ToId, Type: types.CHAIN}
ruleChainRelation := types.RuleNodeRelation{
InId: inNodeId,
OutId: outNodeId,
RelationType: item.Type,
}
// 查询子规则接入节点
nodeRelations, ok := ruleChainCtx.nodeRoutes[inNodeId]
if ok {
nodeRelations = append(nodeRelations, ruleChainRelation)
} else {
nodeRelations = []types.RuleNodeRelation{ruleChainRelation}
}
// 更新关系
ruleChainCtx.nodeRoutes[inNodeId] = nodeRelations
}
// Initialize the root rule context.
// 初始化根节点上下文
if firstNode, ok := ruleChainCtx.GetFirstNode(); ok {
ruleChainCtx.rootRuleContext = NewRuleContext(context.TODO(), ruleChainCtx.config, ruleChainCtx, nil,
firstNode, config.Pool, nil, nil)
} else {
// If there are no nodes, initialize an empty node context.
// 初始化一个空节点上下文
ruleNodeCtx, _ := InitRuleNodeCtx(config, ruleChainCtx, aspects, &types.RuleNode{})
ruleChainCtx.rootRuleContext = NewRuleContext(context.TODO(), ruleChainCtx.config, ruleChainCtx, nil,
ruleNodeCtx, config.Pool, nil, nil)
ruleChainCtx.isEmpty = true
}
return ruleChainCtx, nil
}
推理过程
rulego的核心推理过程,从入口RuleEngine.OnMsg进行处理,核心处理流程如下:
RuleEngine.OnMsg(消息处理入口) -> RuleEngine.onMsgAndWait(核心消息处理) -> DefaultRuleContext.tellOrElse(上下文处理函数) -> DefaultRuleContext.tellNext(节点自处理)-> DefaultRuleContext.NewNextNodeRuleContext(创建节点执行上下文) -> Node.OnMsg(执行节点函数) -> DefaultRuleContext.DoOnEnd(结束执行)
- RuleEngine.onMsgAndWait(核心消息处理)
// engine/engine.go
// onMsgAndWait processes a message through the rule engine, optionally waiting for all nodes to complete.
// It applies any provided RuleContextOptions to customize the execution context.
// 进行核心的规则处理
func (e *RuleEngine) onMsgAndWait(msg types.RuleMsg, wait bool, opts ...types.RuleContextOption) {
// 规则上下文不为空,赋值上下文
if e.rootRuleChainCtx != nil {
// Create a copy of the root context for processing the message.
rootCtx := e.rootRuleChainCtx.rootRuleContext.(*DefaultRuleContext)
// 进行复制
rootCtxCopy := NewRuleContext(
rootCtx.GetContext(),
rootCtx.config,
rootCtx.ruleChainCtx,
rootCtx.from,
rootCtx.self,
rootCtx.pool,
rootCtx.onEnd,
e.ruleChainPool,
)
// 设置是否为第一个
rootCtxCopy.isFirst = rootCtx.isFirst
// 设置运行时闪照
rootCtxCopy.runSnapshot = NewRunSnapshot(msg.Id, rootCtxCopy.ruleChainCtx, time.Now().UnixMilli())
// Apply the provided options to the context copy.
// 进行上下文设置
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(rootCtxCopy)
}
// Handle the case where the rule chain has no nodes.
if rootCtxCopy.ruleChainCtx.isEmpty {
e.onErrHandler(msg, rootCtxCopy, errors.New("the rule chain has no nodes"))
return
}
if rootCtxCopy.initErr != nil {
e.onErrHandler(msg, rootCtxCopy, rootCtxCopy.initErr)
return
}
// Execute start aspects and update the message accordingly.
// 执行启动切片
msg = e.onStart(rootCtxCopy, msg)
// Set up a custom end callback function.
customOnEndFunc := rootCtxCopy.onEnd
// 设置最终结尾处理函数
rootCtxCopy.onEnd = func(ctx types.RuleContext, msg types.RuleMsg, err error, relationType string) {
// Execute end aspects and update the message accordingly.
// 先执行引擎结束处理
msg = e.onEnd(rootCtxCopy, msg, err, relationType)
// Trigger the custom end callback if provided.
if customOnEndFunc != nil {
// 触发终结处理函数
customOnEndFunc(ctx, msg, err, relationType)
}
}
// Set up a custom function to be called upon completion of all nodes.
customFunc := rootCtxCopy.onAllNodeCompleted
// If waiting is required, set up a channel to synchronize the completion.
// 确认等待,则需要所有都执行完了,再继续
if wait {
c := make(chan struct{})
rootCtxCopy.onAllNodeCompleted = func() {
defer close(c)
// Execute the completion handling function.
e.doOnAllNodeCompleted(rootCtxCopy, msg, customFunc)
}
// Process the message through the rule chain.
// 优先处理接下来的
rootCtxCopy.TellNext(msg, rootCtxCopy.firstNodeRelationTypes...)
// Block until all nodes have completed.
<-c
} else {
// If not waiting, simply set the completion handling function.
// 不需要等待,直接异步执行
rootCtxCopy.onAllNodeCompleted = func() {
e.doOnAllNodeCompleted(rootCtxCopy, msg, customFunc)
}
// Process the message through the rule chain.
rootCtxCopy.TellNext(msg, rootCtxCopy.firstNodeRelationTypes...)
}
} else {
// Log an error if the rule engine is not initialized or the root rule chain is not defined.
e.Config.Logger.Printf("onMsg error.RuleEngine not initialized")
}
}
- DefaultRuleContext.tellOrElse(节点自处理)
// tellNext 通知执行子节点,如果是当前第一个节点则执行当前节点
// 如果找不到relationTypes对应的节点,而且defaultRelationType非默认值,则通过defaultRelationType查找节点
func (ctx *DefaultRuleContext) tellOrElse(msg types.RuleMsg, err error, defaultRelationType string, relationTypes ...string) {
//msgCopy := msg.Copy()
if ctx.isFirst {
// 执行自身
ctx.tellSelf(msg, err, relationTypes...)
} else {
if relationTypes == nil {
//找不到子节点,则执行结束回调
ctx.DoOnEnd(msg, err, "")
} else {
for _, relationType := range relationTypes {
//执行After aop
// 返回执行后的结果
msg = ctx.executeAfterAop(msg, err, relationType)
var ok = false
var nodes []types.NodeCtx
//根据relationType查找子节点列表
nodes, ok = ctx.getNextNodes(relationType)
//根据默认关系查找节点
if defaultRelationType != "" && (!ok || len(nodes) == 0) && !ctx.skipTellNext {
nodes, ok = ctx.getNextNodes(defaultRelationType)
}
if ok && !ctx.skipTellNext {
for _, item := range nodes {
tmp := item
//增加一个待执行的子节点
ctx.childReady()
msgCopy := msg.Copy()
//通知执行子节点
ctx.SubmitTack(func() {
ctx.tellNext(msgCopy, tmp, relationType)
})
}
} else {
//找不到子节点,则执行结束回调
ctx.DoOnEnd(msg, err, relationType)
}
}
}
}
}
- DefaultRuleContext.tellNext(节点自处理)
这里主要是进行核心的切片执行与AOP推理
// engine/engine.go
// 执行下一个节点
func (ctx *DefaultRuleContext) tellNext(msg types.RuleMsg, nextNode types.NodeCtx, relationType string) {
defer func() {
//捕捉异常
if e := recover(); e != nil {
//执行After aop
msg = ctx.executeAfterAop(msg, fmt.Errorf("%v", e), relationType)
ctx.childDone()
}
}()
// 创建新的节点上下文
nextCtx := ctx.NewNextNodeRuleContext(nextNode)
//环绕aop
if !nextCtx.executeAroundAop(msg, relationType) {
return
}
// AroundAop 已经执行节点OnMsg逻辑,不再执行下面的逻辑
// 执行节点Msg处理函数
nextNode.OnMsg(nextCtx, msg)
}
- JsTransformNode.OnMsg(节点执行)
具体的执行由节点本身来完成,但是节点中必须使用Next函数进行切换,保证进行下一个节点。核心在于递归式的子节点函数调用与gin中的middle实现思路一致,但是随着调用链的增加,递归栈长度会逐渐加深,内存性能损耗较大,同时对重试机制,分布式step执行不友好。
// OnMsg 处理消息
func (x *JsTransformNode) OnMsg(ctx types.RuleContext, msg types.RuleMsg) {
// 预定义数据
var data interface{} = msg.Data
// 进行数据解析
if msg.DataType == types.JSON {
var dataMap interface{}
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(msg.Data), &dataMap); err == nil {
data = dataMap
} else {
data = make(map[string]interface{})
}
}
// 执行js数据过滤指令
// 获取输出
out, err := x.jsEngine.Execute("Transform", data, msg.Metadata.Values(), msg.Type)
if err != nil {
ctx.TellFailure(msg, err)
} else {
// 转换输出数据为map
formatData, ok := out.(map[string]interface{})
if ok {
// 更新msg对应值
if formatMsgType, ok := formatData[types.MsgTypeKey]; ok {
msg.Type = string2.ToString(formatMsgType)
}
if formatMetaData, ok := formatData[types.MetadataKey]; ok {
msg.Metadata = types.BuildMetadata(string2.ToStringMapString(formatMetaData))
}
if formatMsgData, ok := formatData[types.MsgKey]; ok {
// 设置新值
if newValue, err := string2.ToStringMaybeErr(formatMsgData); err == nil {
msg.Data = newValue
} else {
ctx.TellFailure(msg, err)
return
}
}
// 进行下一步的运算--这个是关键
ctx.TellNext(msg, types.Success)
} else {
ctx.TellFailure(msg, JsTransformReturnFormatErr)
}
}
}