libx264解码学习笔记
参考连接:libx264源码地址;x264主页;x264源代码简单分析;
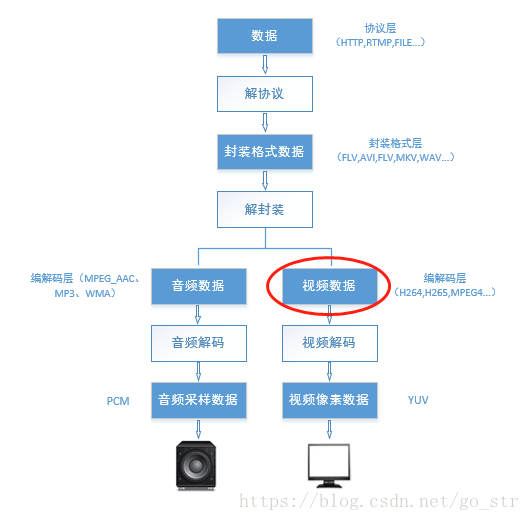
音视频编码在流媒体和网络领域占有重要地位;流媒体编解码流程大致如下图所示:
x264原理解析
H264简介
H.264从1999年开始,到2003年形成草案,最后在2007年定稿有待核实。在ITU的标准里称为H.264,在MPEG的标准里是MPEG-4的一个组成部分–MPEG-4 Part 10,又叫Advanced Video Codec,因此常常称为MPEG-4 AVC或直接叫AVC。x264主要使用算法为H264编解码算法,下面对H264算法进行解析;
H264 编解码解析
参考链接: H264 编解码协议详解;深入浅出理解视频编码H264结构;详细文档;H264编解码框图;
H264编码原理:
在音视频传输过程中,视频文件的传输是一个极大的问题;一段分辨率为19201080,帧率是25的视频,对于传输带宽的要求是:1920108025/8/1024/1024=6.179MB,意味着视频每秒带宽为6.179MB这基本是不肯能的。因此视频压缩和编码技术应运而生。 对于视频文件来说,视频由单张图片帧所组成,每秒25/32帧,但是图片帧的像素块之间存在相似性,因此视频帧图像可以进行图像压缩;H264采用了1616的分块大小对,视频帧图像进行相似比较和压缩编码。如下图所示:

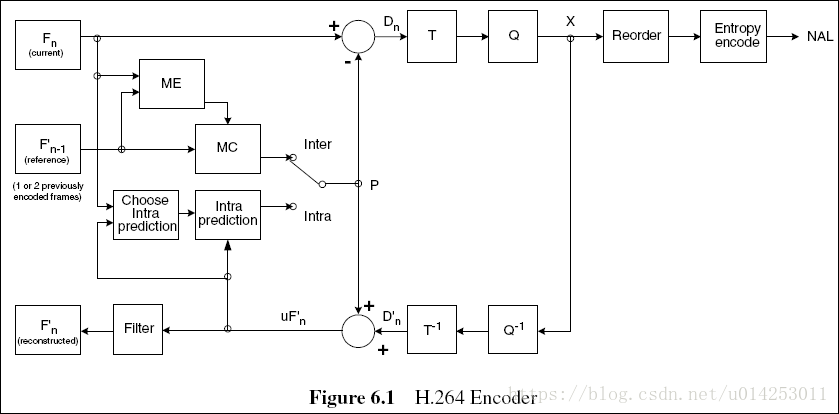
除此之外,对于一段连续的帧图像来说,前一帧和后一帧之间的关联度和相似性很高,只记录当前帧和下一帧与当前帧之间的帧数据差,能够快速的帮助我们实现视频压缩编解码。为了方便图像之间的压缩,将原图像当前帧设置为Fn,下一帧设置为Fn-1;对Fn进行帧内相似压缩编码,使用估计函数进行重新映射(图像还原);再利用当前帧对图和帧差信息对下一帧图片进行估计和还原。具体编码框架如下图:
在上图中,输入的帧或场Fn以宏块为单位被编码器处理。首先,按帧内或者帧间预測编码的方法进行处理。假设採用帧间预測编码,其预測值PRED是由当前片中前面已编码的參考图像经运动补偿(MC)后得到,当中參考图像用F’n-1表示。预測值PRED和当前块相减后,产生一个残差块Dn,经块变换、量化后产生一组量化后的变换系数X,再经熵编码,与解码所需的一些头信息一起组成压缩后的码流,经NAL(网络自适应层)供传输和存储用。
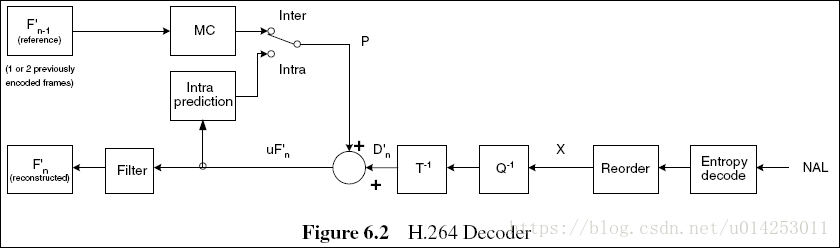
在进行编码过后H264也提供了相应的解码方式,解码流程如下图:
将编码器的NAL输出的H264比特流经熵解码得到量化后的一组变换系数X,再经反量化、反变换,得到残差D’n。利用从该比特流中解码出的头信息,解码器就产生一个预測块PRED,它和编码器中的原始PRED是同样的。当该解码器产生的PRED与残差D’n相加后,就得到了uF’n,再经滤波后,最后就得到滤波后的解码输出图像F’n
H264中的I帧、P帧和B帧
正如上文所说;H264除了使用帧内压缩之外,还使用了帧间压缩;H264采用了独特的I帧、P帧和B帧策略来实现,连续帧之间的压缩;
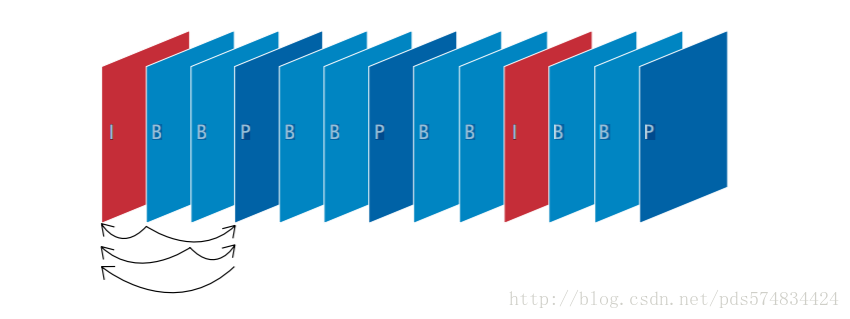
如上图所示;
- I帧:自身可以通过视频解压算法解压成一张单独的完整的图片。
- P帧:需要参考前面的I帧或P帧,还原成完整的图片。
- B帧:需要同时参考前面和后面的I帧或P帧,来实现图片的还原。 H.264基准类中,仅使用I帧和P帧以实现低延时,因此是网络摄像机和视频编码器的理想选择。 注意:每当读取到一个新的I帧时,解码器会更新残差信息,删除之前的东西,防止错误。
H264编码结构解析
H264除了实现了对视频的压缩处理之外,为了方便网络传输,提供了对应的视频编码和分片策略;类似于网络数据封装成IP帧,在H264中将其称为组(gop)、片(slice)、宏块(Macroblock)这些一起组成了H264的码流分层结构;H264将其组织成为序列(GOP)、图片(pictrue)、片(Slice)、宏块(Macroblock)、子块(subblock)五个层次。

H264将视频分为连续的帧进行传输,在连续的帧之间使用I帧、P帧和B帧。同时对于帧内而言,将图像分块为片、宏块和字块进行分片传输;通过这个过程实现对视频文件的压缩包装。

在进行H264分包策略解析之前,我们需要先来了解一下H264的原始码流结构
H264 网络包
参考链接: 从零了解H264结构;H264码流结构分析;
H264在提出视频分片压缩策略的同时,也提出了网络分包发送策略。其详细分包发送策略如下:

下面我们从网络分包的角度对H264原始码流进行分析;
H.264原始码流(裸流)是由一个接一个NALU组成,它的功能分为两层,VCL(视频编码层)和 NAL(网络提取层);
- VCL:包括核心压缩引擎和块,宏块和片的语法级别定义,设计目标是尽可能地独立于网络进行高效的编码;
- NAL:负责将VCL产生的比特字符串适配到各种各样的网络和多元环境中,覆盖了所有片级以上的语法级别。
在VCL进行数据传输或存储之前,这些编码的VCL数据,被映射或封装进NAL单元。(NALU)
一个NALU = 一组对应于视频编码的NALU头部信息 + 一个原始字节序列负荷(RBSP,Raw Byte Sequence Payload).
NALU结构单元的主体结构如下所示;一个原始的H.264 NALU单元常由[StartCode] [NALU Header] [NALU Payload]三部分组成,其中 Start Code 用于标示这是一个NALU 单元的开始,必须是”00 00 00 01” 或”00 00 01”,除此之外基本相当于一个NAL header + RBSP;

NAL Header
由三部分组成,forbidden_bit(1bit),nal_reference_bit(2bits)(优先级),nal_unit_type(5bits)(类型)
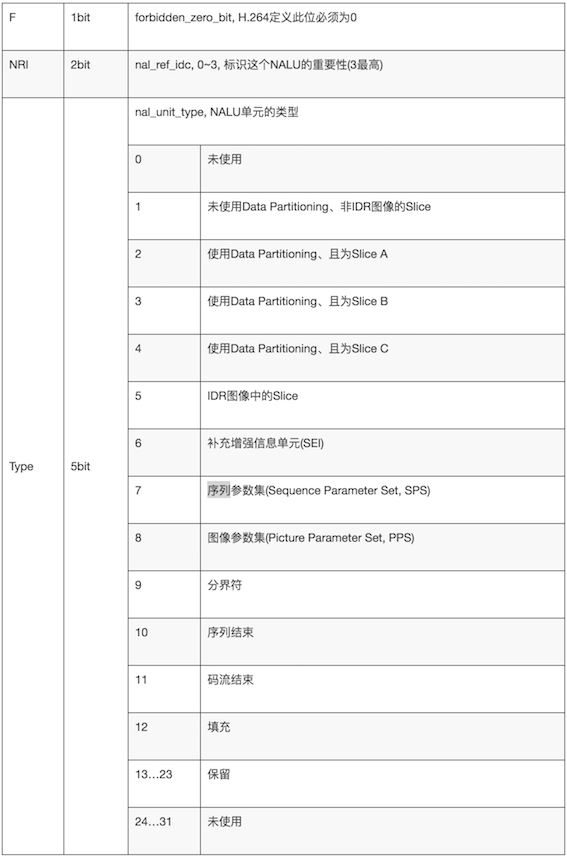


举例如下:
00 00 00 01 06: SEI信息
00 00 00 01 67: 0x67&0x1f = 0x07 :SPS
00 00 00 01 68: 0x68&0x1f = 0x08 :PPS
00 00 00 01 65: 0x65&0x1f = 0x05: IDR Slice
NAL解码流程如下图

RBSP
NALU主体为RBSP;RBSP的主要结构如下:
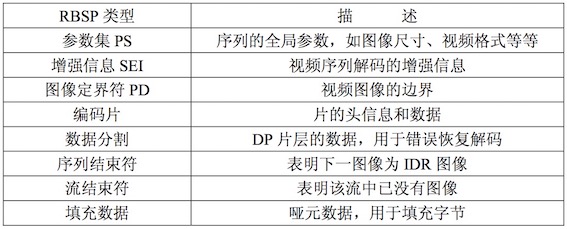
注意:SODB是RBSP的原始帧
- SODB 数据比特串 -> 是编码后的原始数据
- RBSP 原始字节序列载荷 -> 在原始编码数据的后面添加了 结尾比特。一个 bit“1”若干比特“0”,以便字节对齐。

再解H264中的分包策略
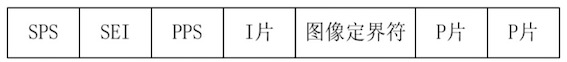
正如图3所示,NALU主体中包含了片头和片上数据
1帧 = n个片
1片 = n个宏块
1宏块 = 16x16yuv数据
片是H.264提出的新概念,通过编码图片后切分通过高效的方式整合出来的概念。一张图片有一个或者多个片,而片由NALU装载并进行网络传输的。但是NALU不一定是切片,这是充分不必要条件,因为 NALU 还有可能装载着其他用作描述视频的信息;片的种类如下表所示
| 片 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| I 片 | 只包含I宏块 |
| P 片 | 包含P和I宏块 |
| B 片 | 包含B和I宏块 |
| SP 片 | 包含P 和/或 I宏块,用于不同码流之间的切换 |
| SI 片 | 一种特殊类型的编码宏块 |
宏块是视频信息的主要承载者。一个编码图像通常划分为多个宏块组成.包含着每一个像素的亮度和色度信息。视频解码最主要的工作则是提供高效的方式从码流中获得宏块中像素阵列。
一个宏块 = 一个16*16的亮度像素 + 一个8×8Cb + 一个8×8Cr彩色像素块组成。(YCbCr 是属于 YUV 家族的一员,在YCbCr 中 Y 是指亮度分量,Cb 指蓝色色度分量,而 Cr 指红色色度分量)
| 宏块分类 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| I 宏块 | 利用从当前片中已解码的像素作为参考进行帧内预测 |
| P 宏块 | 利用前面已编码图像作为参考进行帧内预测,一个帧内编码的宏块可进一步作宏块的分割:即16×16.16×8.8×16.8×8亮度像素块。如果选了8×8的子宏块,则可再分成各种子宏块的分割,其尺寸为8×8,8×4,4×8,4×4 |
| B 宏块 | 利用双向的参考图像(当前和未来的已编码图像帧)进行帧内预测 |
句法元素的分层结构有助于更有效地节省码流。例如,再一个图像中,经常会在各个片之间有相同的数据,如果每个片都同时携带这些数据,势必会造成码流的浪费。更为有效的做法是将该图像的公共信息抽取出来,形成图像一级的句法元素,而在片级只携带该片自身独有的句法元素。


| 宏块分类 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| mb_type | 确定该 MB 是帧内或帧间(P 或 B)编码模式,确定该 MB 分割的尺寸 |
| mb_pred | 确定帧内预测模式(帧内宏块)确定表 0 或表 1 参考图 像,和每一宏块分割的差分编码的运动矢量(帧间宏块,除 8×8 宏块分割的帧内 MB) |
| sub_mb_pred | (只对 8×8MB 分割的帧内 MB)确定每一子宏块的子宏 块分割,每一宏块分割的表 0 和/或表 1 的参考图象;每一 宏块子分割的差分编码运动矢量。 |
| coded_block_pattern | 指出哪个 8×8 块(亮度和彩色)包 编码变换系数 |
| mb_qp_delta | 量化参数的改变值 |
| residual | 预测后对应于残差图象取样的编码变换系数 |
I,P,B帧与pts/dts
| 帧的分类 | 中文 | 意义 |
|---|---|---|
| I帧 | 帧内编码帧,又称intra picture | I 帧通常是每个 GOP(MPEG 所使用的一种视频压缩技术)的第一个帧,经过适度地压缩,做为随机访问的参考点,可以当成图象。I帧可以看成是一个图像经过压缩后的产物 |
| P帧 | 前向预测编码帧,又称predictive-frame | 通过充分将低于图像序列中前面已编码帧的时间冗余信息来压缩传输数据量的编码图像,也叫预测帧 |
| B帧 | 双向预测帧,又称bi-directional interpolated prediction frame | 既考虑与源图像序列前面已编码帧,也顾及源图像序列后面已编码帧之间的时间冗余信息来压缩传输数据量的编码图像,也叫双向预测帧 |
I,P,B帧的不同
- I frame:自身可以通过视频解压算法解压成一张单独的完整的图片。
- P frame:需要参考其前面的一个I frame 或者B frame来生成一张完整的图片。
- B frame:则要参考其前一个I或者P帧及其后面的一个P帧来生成一张完整的图片。
pts/dts
| 名称 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| PTS(Presentation Time Stamp) | PTS主要用于度量解码后的视频帧什么时候被显示出来。 |
| DTS(Decode Time Stamp) | DTS主要是标识内存中的bit流再什么时候开始送入解码器中进行解码。 |

主要区别:DTS主要用户视频的解码,在解码阶段使用。PTS主要用于视频的同步和输出,在display的时候使用。再没有B frame的时候输出顺序一样。
IDR 一个序列的第一个图像叫做 IDR 图像(立即刷新图像),IDR 图像都是 I 帧图像。 I和IDR帧都使用帧内预测。I帧不用参考任何帧,但是之后的P帧和B帧是有可能参考这个I帧之前的帧的。IDR就不允许这样。 其核心作用是,是为了解码的重同步,当解码器解码到 IDR 图像时,立即将参考帧队列清空,将已解码的数据全部输出或抛弃,重新查找参数集,开始一个新的序列。这样,如果前一个序列出现重大错误,在这里可以获得重新同步的机会。IDR图像之后的图像永远不会使用IDR之前的图像的数据来解码。
帧(frame)和场(filed)
参考链接: 帧编码与场编码的区别分析
视频的一场和一帧用来产生一个编码图像,一帧通常是一个完整的图像,当采集视频信号时,如果采用隔行扫描(奇、偶数行),则扫描下来的一帧图像就被分成了两个部分,这每一部分都被称为 [场],根据次序,分为 [顶场] 和 [底场]。 人眼可察觉到的电视视频图像刷新中的闪烁为 0.02 秒,即当电视系统的帧率低于 50 帧/秒,人眼可感觉得出画面的闪烁。常规如 PAL 制式电视系统帧率为 25 帧/秒、NTSC 制式的则为 30 帧/秒,如果采用逐行扫描将不可避免地在视频刷新时产生闪烁现象。而另一方面如果单纯的提高帧率达到避免闪烁刷新效果,则会增加系统的频带宽度。 隔行扫描中,每一帧包含两个场(top field)和(bottom field),其中每个 field 包含一帧中一半数量的水平线,top field 包含所有奇数线,bottom field 则包含所有偶数线。则在电视显示过程中,电子枪每发射一行隔一行—先发射奇数行13579…(top field)回头再发射2468…(bottom field)利用两次扫描来完成一幅图像,因为视觉的滞留性,我们看到的效果是差不多的。如在 NTSC 视频中 frame 的频率为30次/秒-àfield的频率则为 60 次/秒,大于了人眼可察觉闪烁的频率。
| 方式 | 作用域 |
|---|---|
| 帧编码方式 | 活动量较小或者静止的图像宜采用 |
| 场编码方式 | 活动量较大的运动图像 |

H264编解码编程
参考链接: x264源代码简单分析:概述; 开源的H264编码器有很多,JMVC,T264、X264,这里选择X264,因为网上关于X264源码分析资源很多。X264编码器是一个开源的经过优化的高性能H.264编码器,目前最新的源码在本人的I5处理器的PC机上,编码1920x1080分辨率的视频序列在使用ultrafast配置的情况下,可以实现160fps左右的编码速度。 H264编码规范,已经有了不错的编解码实现;其中承担编码任务的主要实现有:x264,解码主要实现有libavcodec;下面分别对这两个进行介绍。
x264说明和API详解
x264命令行使用和参数解析
参考链接: X264 01 命令行用法 使用linux 中使用x264时可以直接使用:
x264 --fullhelp //
查看x264帮助信息;显示内容如下
x264 core:148 r2643 5c65704
Syntax: x264 [options] -o outfile infile
Infile can be raw (in which case resolution is required),
or YUV4MPEG (*.y4m),
or Avisynth if compiled with support (yes).
or libav* formats if compiled with lavf support (yes) or ffms support (yes).
Outfile type is selected by filename:
.264 -> Raw bytestream
.mkv -> Matroska
.flv -> Flash Video
.mp4 -> MP4 if compiled with GPAC or L-SMASH support (gpac)
Output bit depth: 8 (configured at compile time)
Options:
-h, --help List basic options
--longhelp List more options
--fullhelp List all options
Example usage:
Constant quality mode:
x264 --crf 24 -o <output> <input>
Two-pass with a bitrate of 1000kbps:
x264 --pass 1 --bitrate 1000 -o <output> <input>
x264 --pass 2 --bitrate 1000 -o <output> <input>
Lossless:
x264 --qp 0 -o <output> <input>
Maximum PSNR at the cost of speed and visual quality:
x264 --preset placebo --tune psnr -o <output> <input>
Constant bitrate at 1000kbps with a 2 second-buffer:
x264 --vbv-bufsize 2000 --bitrate 1000 -o <output> <input>
Presets:
--profile <string> Force the limits of an H.264 profile
Overrides all settings.
- baseline:
--no-8x8dct --bframes 0 --no-cabac
--cqm flat --weightp 0
No interlaced.
No lossless.
- main:
--no-8x8dct --cqm flat
No lossless.
- high:
No lossless.
- high10:
No lossless.
Support for bit depth 8-10.
- high422:
No lossless.
Support for bit depth 8-10.
Support for 4\:2\:0/4\:2\:2 chroma subsampling.
- high444:
Support for bit depth 8-10.
Support for 4\:2\:0/4\:2\:2/4\:4\:4 chroma subsampling.
--preset <string> Use a preset to select encoding settings [medium]
Overridden by user settings.
- ultrafast:
--no-8x8dct --aq-mode 0 --b-adapt 0
--bframes 0 --no-cabac --no-deblock
--no-mbtree --me dia --no-mixed-refs
--partitions none --rc-lookahead 0 --ref 1
--scenecut 0 --subme 0 --trellis 0
--no-weightb --weightp 0
- superfast:
--no-mbtree --me dia --no-mixed-refs
--partitions i8x8,i4x4 --rc-lookahead 0
--ref 1 --subme 1 --trellis 0 --weightp 1
- veryfast:
--no-mixed-refs --rc-lookahead 10
--ref 1 --subme 2 --trellis 0 --weightp 1
- faster:
--no-mixed-refs --rc-lookahead 20
--ref 2 --subme 4 --weightp 1
- fast:
--rc-lookahead 30 --ref 2 --subme 6
--weightp 1
- medium:
Default settings apply.
- slow:
--b-adapt 2 --direct auto --me umh
--rc-lookahead 50 --ref 5 --subme 8
- slower:
--b-adapt 2 --direct auto --me umh
--partitions all --rc-lookahead 60
--ref 8 --subme 9 --trellis 2
- veryslow:
--b-adapt 2 --bframes 8 --direct auto
--me umh --merange 24 --partitions all
--ref 16 --subme 10 --trellis 2
--rc-lookahead 60
- placebo:
--bframes 16 --b-adapt 2 --direct auto
--slow-firstpass --no-fast-pskip
--me tesa --merange 24 --partitions all
--rc-lookahead 60 --ref 16 --subme 11
--trellis 2
--tune <string> Tune the settings for a particular type of source
or situation
Overridden by user settings.
Multiple tunings are separated by commas.
Only one psy tuning can be used at a time.
- film (psy tuning):
--deblock -1:-1 --psy-rd <unset>:0.15
- animation (psy tuning):
--bframes {+2} --deblock 1:1
--psy-rd 0.4:<unset> --aq-strength 0.6
--ref {Double if >1 else 1}
- grain (psy tuning):
--aq-strength 0.5 --no-dct-decimate
--deadzone-inter 6 --deadzone-intra 6
--deblock -2:-2 --ipratio 1.1
--pbratio 1.1 --psy-rd <unset>:0.25
--qcomp 0.8
- stillimage (psy tuning):
--aq-strength 1.2 --deblock -3:-3
--psy-rd 2.0:0.7
- psnr (psy tuning):
--aq-mode 0 --no-psy
- ssim (psy tuning):
--aq-mode 2 --no-psy
- fastdecode:
--no-cabac --no-deblock --no-weightb
--weightp 0
- zerolatency:
--bframes 0 --force-cfr --no-mbtree
--sync-lookahead 0 --sliced-threads
--rc-lookahead 0
--slow-firstpass Do not force these faster settings with --pass 1:
--no-8x8dct --me dia --partitions none
--ref 1 --subme {2 if >2 else unchanged}
--trellis 0 --fast-pskip
Frame-type options:
-I, --keyint <integer or "infinite"> Maximum GOP size [250]
-i, --min-keyint <integer> Minimum GOP size [auto]
--no-scenecut Disable adaptive I-frame decision
--scenecut <integer> How aggressively to insert extra I-frames [40]
--intra-refresh Use Periodic Intra Refresh instead of IDR frames
-b, --bframes <integer> Number of B-frames between I and P [3]
--b-adapt <integer> Adaptive B-frame decision method [1]
Higher values may lower threading efficiency.
- 0: Disabled
- 1: Fast
- 2: Optimal (slow with high --bframes)
--b-bias <integer> Influences how often B-frames are used [0]
--b-pyramid <string> Keep some B-frames as references [normal]
- none: Disabled
- strict: Strictly hierarchical pyramid
- normal: Non-strict (not Blu-ray compatible)
--open-gop Use recovery points to close GOPs
Only available with b-frames
--no-cabac Disable CABAC
-r, --ref <integer> Number of reference frames [3]
--no-deblock Disable loop filter
-f, --deblock <alpha:beta> Loop filter parameters [0:0]
--slices <integer> Number of slices per frame; forces rectangular
slices and is overridden by other slicing options
--slices-max <integer> Absolute maximum slices per frame; overrides
slice-max-size/slice-max-mbs when necessary
--slice-max-size <integer> Limit the size of each slice in bytes
--slice-max-mbs <integer> Limit the size of each slice in macroblocks (max)
--slice-min-mbs <integer> Limit the size of each slice in macroblocks (min)
--tff Enable interlaced mode (top field first)
--bff Enable interlaced mode (bottom field first)
--constrained-intra Enable constrained intra prediction.
--pulldown <string> Use soft pulldown to change frame rate
- none, 22, 32, 64, double, triple, euro (requires cfr input)
--fake-interlaced Flag stream as interlaced but encode progressive.
Makes it possible to encode 25p and 30p Blu-Ray
streams. Ignored in interlaced mode.
--frame-packing <integer> For stereoscopic videos define frame arrangement
- 0: checkerboard - pixels are alternatively from L and R
- 1: column alternation - L and R are interlaced by column
- 2: row alternation - L and R are interlaced by row
- 3: side by side - L is on the left, R on the right
- 4: top bottom - L is on top, R on bottom
- 5: frame alternation - one view per frame
- 6: mono - 2D frame without any frame packing
- 7: tile format - L is on top-left, R split across
Ratecontrol:
-q, --qp <integer> Force constant QP (0-69, 0=lossless)
-B, --bitrate <integer> Set bitrate (kbit/s)
--crf <float> Quality-based VBR (0-51) [23.0]
--rc-lookahead <integer> Number of frames for frametype lookahead [40]
--vbv-maxrate <integer> Max local bitrate (kbit/s) [0]
--vbv-bufsize <integer> Set size of the VBV buffer (kbit) [0]
--vbv-init <float> Initial VBV buffer occupancy [0.9]
--crf-max <float> With CRF+VBV, limit RF to this value
May cause VBV underflows!
--qpmin <integer> Set min QP [0]
--qpmax <integer> Set max QP [69]
--qpstep <integer> Set max QP step [4]
--ratetol <float> Tolerance of ABR ratecontrol and VBV [1.0]
--ipratio <float> QP factor between I and P [1.40]
--pbratio <float> QP factor between P and B [1.30]
--chroma-qp-offset <integer> QP difference between chroma and luma [0]
--aq-mode <integer> AQ method [1]
- 0: Disabled
- 1: Variance AQ (complexity mask)
- 2: Auto-variance AQ
- 3: Auto-variance AQ with bias to dark scenes
--aq-strength <float> Reduces blocking and blurring in flat and
textured areas. [1.0]
-p, --pass <integer> Enable multipass ratecontrol
- 1: First pass, creates stats file
- 2: Last pass, does not overwrite stats file
- 3: Nth pass, overwrites stats file
--stats <string> Filename for 2 pass stats ["x264_2pass.log"]
--no-mbtree Disable mb-tree ratecontrol.
--qcomp <float> QP curve compression [0.60]
--cplxblur <float> Reduce fluctuations in QP (before curve compression) [20.0]
--qblur <float> Reduce fluctuations in QP (after curve compression) [0.5]
--zones <zone0>/<zone1>/... Tweak the bitrate of regions of the video
Each zone is of the form
<start frame>,<end frame>,<option>
where <option> is either
q=<integer> (force QP)
or b=<float> (bitrate multiplier)
--qpfile <string> Force frametypes and QPs for some or all frames
Format of each line: framenumber frametype QP
QP is optional (none lets x264 choose). Frametypes: I,i,K,P,B,b.
K=<I or i> depending on open-gop setting
QPs are restricted by qpmin/qpmax.
Analysis:
-A, --partitions <string> Partitions to consider ["p8x8,b8x8,i8x8,i4x4"]
- p8x8, p4x4, b8x8, i8x8, i4x4
- none, all
(p4x4 requires p8x8. i8x8 requires --8x8dct.)
--direct <string> Direct MV prediction mode ["spatial"]
- none, spatial, temporal, auto
--no-weightb Disable weighted prediction for B-frames
--weightp <integer> Weighted prediction for P-frames [2]
- 0: Disabled
- 1: Weighted refs
- 2: Weighted refs + Duplicates
--me <string> Integer pixel motion estimation method ["hex"]
- dia: diamond search, radius 1 (fast)
- hex: hexagonal search, radius 2
- umh: uneven multi-hexagon search
- esa: exhaustive search
- tesa: hadamard exhaustive search (slow)
--merange <integer> Maximum motion vector search range [16]
--mvrange <integer> Maximum motion vector length [-1 (auto)]
--mvrange-thread <int> Minimum buffer between threads [-1 (auto)]
-m, --subme <integer> Subpixel motion estimation and mode decision [7]
- 0: fullpel only (not recommended)
- 1: SAD mode decision, one qpel iteration
- 2: SATD mode decision
- 3-5: Progressively more qpel
- 6: RD mode decision for I/P-frames
- 7: RD mode decision for all frames
- 8: RD refinement for I/P-frames
- 9: RD refinement for all frames
- 10: QP-RD - requires trellis=2, aq-mode>0
- 11: Full RD: disable all early terminations
--psy-rd <float:float> Strength of psychovisual optimization ["1.0:0.0"]
#1: RD (requires subme>=6)
#2: Trellis (requires trellis, experimental)
--no-psy Disable all visual optimizations that worsen
both PSNR and SSIM.
--no-mixed-refs Do not decide references on a per partition basis
--no-chroma-me Ignore chroma in motion estimation
--no-8x8dct Disable adaptive spatial transform size
-t, --trellis <integer> Trellis RD quantization. [1]
- 0: disabled
- 1: enabled only on the final encode of a MB
- 2: enabled on all mode decisions
--no-fast-pskip Disables early SKIP detection on P-frames
--no-dct-decimate Disables coefficient thresholding on P-frames
--nr <integer> Noise reduction [0]
--deadzone-inter <int> Set the size of the inter luma quantization deadzone [21]
--deadzone-intra <int> Set the size of the intra luma quantization deadzone [11]
Deadzones should be in the range 0 - 32.
--cqm <string> Preset quant matrices ["flat"]
- jvt, flat
--cqmfile <string> Read custom quant matrices from a JM-compatible file
Overrides any other --cqm* options.
--cqm4 <list> Set all 4x4 quant matrices
Takes a comma-separated list of 16 integers.
--cqm8 <list> Set all 8x8 quant matrices
Takes a comma-separated list of 64 integers.
--cqm4i, --cqm4p, --cqm8i, --cqm8p <list>
Set both luma and chroma quant matrices
--cqm4iy, --cqm4ic, --cqm4py, --cqm4pc <list>
Set individual quant matrices
Video Usability Info (Annex E):
The VUI settings are not used by the encoder but are merely suggestions to
the playback equipment. See doc/vui.txt for details. Use at your own risk.
--overscan <string> Specify crop overscan setting ["undef"]
- undef, show, crop
--videoformat <string> Specify video format ["undef"]
- component, pal, ntsc, secam, mac, undef
--range <string> Specify color range ["auto"]
- auto, tv, pc
--colorprim <string> Specify color primaries ["undef"]
- undef, bt709, bt470m, bt470bg, smpte170m,
smpte240m, film, bt2020
--transfer <string> Specify transfer characteristics ["undef"]
- undef, bt709, bt470m, bt470bg, smpte170m,
smpte240m, linear, log100, log316,
iec61966-2-4, bt1361e, iec61966-2-1,
bt2020-10, bt2020-12
--colormatrix <string> Specify color matrix setting ["???"]
- undef, bt709, fcc, bt470bg, smpte170m,
smpte240m, GBR, YCgCo, bt2020nc, bt2020c
--chromaloc <integer> Specify chroma sample location (0 to 5) [0]
--nal-hrd <string> Signal HRD information (requires vbv-bufsize)
- none, vbr, cbr (cbr not allowed in .mp4)
--filler Force hard-CBR and generate filler (implied by
--nal-hrd cbr)
--pic-struct Force pic_struct in Picture Timing SEI
--crop-rect <string> Add 'left,top,right,bottom' to the bitstream-level
cropping rectangle
Input/Output:
-o, --output <string> Specify output file
--muxer <string> Specify output container format ["auto"]
- auto, raw, mkv, flv, mp4
--demuxer <string> Specify input container format ["auto"]
- auto, raw, y4m, avs, lavf, ffms
--input-fmt <string> Specify input file format (requires lavf support)
--input-csp <string> Specify input colorspace format for raw input
- valid csps for `raw` demuxer:
i420, yv12, nv12, nv21, i422, yv16, nv16, i444, yv24, bgr, bgra, rgb
- valid csps for `lavf` demuxer:
yuv420p, yuyv422, rgb24, bgr24, yuv422p,
yuv444p, yuv410p, yuv411p, gray, monow, monob,
pal8, yuvj420p, yuvj422p, yuvj444p, xvmcmc,
xvmcidct, uyvy422, uyyvyy411, bgr8, bgr4,
bgr4_byte, rgb8, rgb4, rgb4_byte, nv12, nv21,
argb, rgba, abgr, bgra, gray16be, gray16le,
yuv440p, yuvj440p, yuva420p, vdpau_h264,
vdpau_mpeg1, vdpau_mpeg2, vdpau_wmv3,
vdpau_vc1, rgb48be, rgb48le, rgb565be,
rgb565le, rgb555be, rgb555le, bgr565be,
bgr565le, bgr555be, bgr555le, vaapi_moco,
vaapi_idct, vaapi_vld, yuv420p16le,
yuv420p16be, yuv422p16le, yuv422p16be,
yuv444p16le, yuv444p16be, vdpau_mpeg4,
dxva2_vld, rgb444le, rgb444be, bgr444le,
bgr444be, ya8, bgr48be, bgr48le, yuv420p9be,
yuv420p9le, yuv420p10be, yuv420p10le,
yuv422p10be, yuv422p10le, yuv444p9be,
yuv444p9le, yuv444p10be, yuv444p10le,
yuv422p9be, yuv422p9le, vda_vld, gbrp, gbrp9be,
gbrp9le, gbrp10be, gbrp10le, gbrp16be,
gbrp16le, yuva420p9be, yuva420p9le,
yuva422p9be, yuva422p9le, yuva444p9be,
yuva444p9le, yuva420p10be, yuva420p10le,
yuva422p10be, yuva422p10le, yuva444p10be,
yuva444p10le, yuva420p16be, yuva420p16le,
yuva422p16be, yuva422p16le, yuva444p16be,
yuva444p16le, vdpau, xyz12le, xyz12be, nv16,
nv20le, nv20be, yvyu422, vda, ya16be, ya16le,
qsv, mmal, d3d11va_vld, rgba64be, rgba64le,
bgra64be, bgra64le, 0rgb, rgb0, 0bgr, bgr0,
yuva444p, yuva422p, yuv420p12be, yuv420p12le,
yuv420p14be, yuv420p14le, yuv422p12be,
yuv422p12le, yuv422p14be, yuv422p14le,
yuv444p12be, yuv444p12le, yuv444p14be,
yuv444p14le, gbrp12be, gbrp12le, gbrp14be,
gbrp14le, gbrap, gbrap16be, gbrap16le,
yuvj411p, bayer_bggr8, bayer_rggb8,
bayer_gbrg8, bayer_grbg8, bayer_bggr16le,
bayer_bggr16be, bayer_rggb16le, bayer_rggb16be,
bayer_gbrg16le, bayer_gbrg16be, bayer_grbg16le,
bayer_grbg16be, yuv440p10le, yuv440p10be,
yuv440p12le, yuv440p12be, ayuv64le, ayuv64be,
videotoolbox_vld
--output-csp <string> Specify output colorspace ["i420"]
- i420, i422, i444, rgb
--input-depth <integer> Specify input bit depth for raw input
--input-range <string> Specify input color range ["auto"]
- auto, tv, pc
--input-res <intxint> Specify input resolution (width x height)
--index <string> Filename for input index file
--sar width:height Specify Sample Aspect Ratio
--fps <float|rational> Specify framerate
--seek <integer> First frame to encode
--frames <integer> Maximum number of frames to encode
--level <string> Specify level (as defined by Annex A)
--bluray-compat Enable compatibility hacks for Blu-ray support
--avcintra-class <integer> Use compatibility hacks for AVC-Intra class
- 50, 100, 200
--stitchable Do not optimize headers based on video content
Ensures ability to recombine a segmented encode
-v, --verbose Print stats for each frame
--no-progress Do not show the progress indicator while encoding
--quiet Quiet Mode
--log-level <string> Specify the maximum level of logging ["info"]
- none, error, warning, info, debug
--psnr Enable PSNR computation
--ssim Enable SSIM computation
--threads <integer> Force a specific number of threads
--lookahead-threads <integer> Force a specific number of lookahead threads
--sliced-threads Low-latency but lower-efficiency threading
--thread-input Run Avisynth in its own thread
--sync-lookahead <integer> Number of buffer frames for threaded lookahead
--non-deterministic Slightly improve quality of SMP, at the cost of repeatability
--cpu-independent Ensure exact reproducibility across different cpus,
as opposed to letting them select different algorithms
--asm <integer> Override CPU detection
--no-asm Disable all CPU optimizations
--opencl Enable use of OpenCL
--opencl-clbin <string> Specify path of compiled OpenCL kernel cache
--opencl-device <integer> Specify OpenCL device ordinal
--dump-yuv <string> Save reconstructed frames
--sps-id <integer> Set SPS and PPS id numbers [0]
--aud Use access unit delimiters
--force-cfr Force constant framerate timestamp generation
--tcfile-in <string> Force timestamp generation with timecode file
--tcfile-out <string> Output timecode v2 file from input timestamps
--timebase <int/int> Specify timebase numerator and denominator
<integer> Specify timebase numerator for input timecode file
or specify timebase denominator for other input
--dts-compress Eliminate initial delay with container DTS hack
Filtering:
--vf, --video-filter <filter0>/<filter1>/... Apply video filtering to the input file
Filter options may be specified in <filter>:<option>=<value> format.
Available filters:
crop:left,top,right,bottom
removes pixels from the edges of the frame
resize:[width,height][,sar][,fittobox][,csp][,method]
resizes frames based on the given criteria:
- resolution only: resizes and adapts sar to avoid stretching
- sar only: sets the sar and resizes to avoid stretching
- resolution and sar: resizes to given resolution and sets the sar
- fittobox: resizes the video based on the desired constraints
- width, height, both
- fittobox and sar: same as above except with specified sar
- csp: convert to the given csp. syntax: [name][:depth]
- valid csp names [keep current]: i420, yv12, nv12, nv21, i422, yv16, nv16, i444, yv24, bgr, bgra, rgb
- depth: 8 or 16 bits per pixel [keep current]
note: not all depths are supported by all csps.
- method: use resizer method ["bicubic"]
- fastbilinear, bilinear, bicubic, experimental, point,
- area, bicublin, gauss, sinc, lanczos, spline
select_every:step,offset1[,...]
apply a selection pattern to input frames
step: the number of frames in the pattern
offsets: the offset into the step to select a frame
see: http://avisynth.nl/index.php/Select#SelectEvery
基本使用方法:
x264 [options] -o outfile infile
# 可以输出为一下四种格式
Outfile type is selected by filename:
.264 -> Raw bytestream
.mkv -> Matroska
.flv -> Flash Video
.mp4 -> MP4 if compiled with GPAC or L-SMASH support (no)
基本参数说明:
-
--bitrate:指定码率,使用示例:x264 --bitrate 1000 -o output.264 input_640x360_yuv420p.yuv; -
--fps:指定帧率,使用示例:x264 --fps 10 -o output.264 input_640x360_yuv420p.yuv -
--preset:指定编码速度,--preset的参数主要调节编码速度和质量的平衡;使用示例:x264 --preset ultrafast -o output.264 input_640x360_yuv420p.yuv -
--tune:融合视觉优化,tune的值有:-
film:电影、真人类型 -
animation:动画 -
grain:需要保留大量的grain -
stillimage:静态图像编码时使用 -
psnr:为提高psnr做了参数上的优化 -
ssim:为提高ssim做了优化的参数 - fastecode:可以快速解码的参数
- zerolatency:0延迟,用在需要非常低的延迟的情况下,比如电视电话会议的编码。
-
详细参数说明
1. prfile(档次)
| 序 | name | 名称 | 8x8dct | cqm | bframes | cabac | weightp | interlaced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | baseline | 基线 | no | flat | 0 | no | 0 | no |
| 2 | main | 主要 | no | flat | 不限 | 不限 | 不限 | 不限 |
| 3 | high | 高 | 不限 | 不限 | 不限 | 不限 | 不限 | 不限 |
| 4 | high10 | 高10位 | 不限 | 不限 | 不限 | 不限 | 不限 | 不限 |
详解:
- bframes:在I帧与P帧之间可插入B帧数量(Number of B-frames)的最大值,范围0-16。
- cqm:自订量化矩阵(custom quantization matrices)。默认有flat和JVT。
- weightp:使x264能够使用明确加权预测(explicit weighted prediction)来改善P帧的压缩。亦改善淡入/淡出的品质。模式越高越慢。
- 8x8dct:弹性8x8离散余弦转换(Adaptive 8x8 DCT)
- cabac:弹性内容的二进制算数编码(CABAC:Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coder)。
- interlaced:隔行扫描。
2 preset(预设)
| 序 | name | 名称 | b-adapt | bframes | direct | me | merange | partitions | rc-lookahead | ref | subme | trellis | weightp | other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ultrafast | 极快 | 0 | 0 | dia | none | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | no-8x8dct aq-mode0 no-cabac no-deblock no-mbtree no-mixed-refs scenecut0 no-weightb | ||
| 2 | superfast | 超快 | dia | i8x8,i4x4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | no-mixed-refsno-mbtree | ||||
| 3 | veryfast | 很快 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | no-mixed-refs | ||||||
| 4 | faster | 较快 | 20 | 2 | 4 | 1 | no-mixed-refs | |||||||
| 5 | fast | 快 | 30 | 2 | 6 | 1 | ||||||||
| 6 | medium | 中 | ||||||||||||
| 7 | slow | 慢 | 2 | auto | umh | 50 | 5 | 8 | ||||||
| 8 | slower | 较慢 | 2 | auto | umh | all | 60 | 8 | 9 | 2 | ||||
| 9 | veryslow | 很慢 | 2 | 8 | auto | umh | 24 | all 60 | 16 | 10 | 2 | |||
| 10 | placebo | 2 | 16 | auto | tesa | 24 | all | 60 | 16 | 11 | 2 | slow-firstpass no-fast-pskip |
参数详解:
-
b-adapt:设定弹性B帧位置决策算法。此设定控制x264如何决定要放置P帧或B帧。 -
bframes:在I帧与P帧之间可插入B帧数量(Number of B-frames)的最大值,范围0-16。 -
direct:”direct”动态向量(motion vectors)的预测模式。有两种模式可用:spatial和temporal。可以指定none来停用direct动态向量,和指定auto来允许x264在两者之间切换为适合的模式。 -
me:全像素(full-pixel)运动估计(motion estimation)的算法。 -
merange:控制运动估计的最大范围(单位是像素)。对于hex和dia,范围限制在4~16。对于umh和esa,它可以增加到超过默认值16来允许范围更广的动态搜寻,对于HD视讯和高动态镜头很有用。注意,对于umh、esa和tesa,增加merange会大幅减慢编码速度。 -
partitions:H.264视讯在压缩过程中划分为16x16的宏区块。这些区块可以进一步划分为更小的分割,这就是此选项要控制的部分。 -
rc-lookahead:设定mb-tree位元率控制和vbv-lookahead使用的帧数。最大允许值是250。对于mb-tree部分,增加帧数带来更好的效果但也会更慢。mb-tree使用的最大缓冲值是MIN(rc-lookahead, --keyint)。 -
ref:控制解码图片缓冲(DPB:Decoded Picture Buffer)的大小。范围是从0到16。总之,此值是每个P帧可以使用先前多少帧作为参照帧的数目(B帧可以使用的数目要少一或两个,取决于它们是否作为参照帧)。可以被参照的最小ref数是1。 -
subme:设定子像素(subpixel)估算复杂度。值越高越好。层级1~5只是控制子像素细分(refinement)强度。层级6为模式决策启用RDO,而层级8为动态向量和内部预测模式启用RDO。RDO层级明显慢于先前的层级。 -trellis:执行Trellis quantization来提高效率。 -
weightp:使x264能够使用明确加权预测(explicit weighted prediction)来改善P帧的压缩。亦改善淡入/淡出的品质。模式越高越慢。 -
no-8x8dct:停用弹性8x8离散余弦转换(Adaptive 8x8 DCT)。 -
aq-mode:弹性量化模式。没有AQ时,x264很容易分配不足的位元数到细节较少的部分。AQ是用来更好地分配视讯里所有宏区块之间的可用位元数。 -
no-cabac:停用弹性内容的二进制算数编码(CABAC:Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coder)资料流压缩,切换回效率较低的弹性内容的可变长度编码(CAVLC:Context Adaptive Variable Length Coder)系统。大幅降低压缩效率(通常10~20%)和解码的硬件需求。 -
no-deblock:停用循环筛选(loop filter。亦称为持续循环去区块(inloop deblocker))。 -
no-mbtree:停用宏区块树(macroblock tree)位元率控制。使用宏区块树位元率控制会改善整体压缩率,借由追踪跨帧的时间传播(temporal propagation)并相应地加权。 -
no-mixed-refs:混合参照会以每个8x8分割为基础来选取参照,而不是以每个宏区块为基础。当使用多个参照帧时这会改善品质,虽然要损失一些速度。设定此选项会停用该功能。 -
scenecut:设定I/IDR帧位置的阈值(场景变更侦测)。 -
no-weightb:停用“加权”B帧的参照。 -
slow-firstpass:慢速pass。 -
no-fast-pskip:停用P帧的早期略过侦测(early skip detection)。非常轻微地提高品质,但要损失很多速度。
3 tune(调校)
| 序 | name | 名称 | ref | bframes | deblock | psy-rd | aq-strength | other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | film | 电影 | -1:-1 | 0.15 | ||||
| 2 | animation | 动画 | {Double if >1 else 1} | {+2} | 1:1 | 0.4 | 0.6 | |
| 3 | grain | 颗粒 | -2:-2 | 0.25 | 0.5 | no-dct-decimate deadzone-inter6 deadzone-intra6 ipratio1.1 pbratio1.1 qcomp0.8 | ||
| 4 | stillimage | 静态图像 | -3:-3 | 2.0:0.7 | 1.2 | |||
| 5 | psnr | PSNR测试 | no | aq-mode0 | ||||
| 6 | ssim | SSIM测试 | no | aq-mode2 | ||||
| 7 | fastdecode | 快速解码 | no | no-cabac no-weightb weightp0 | ||||
| 8 | zerolatency | 零延迟 | 0 | force-cfr no-mbtree sync-lookahead0 sliced-threads rc-lookahead0 |
-
ref:控制解码图片缓冲(DPB:Decoded Picture Buffer)的大小。范围是从0到16。总之,此值是每个P帧可以使用先前多少帧作为参照帧的数目(B帧可以使用的数目要少一或两个,取决于它们是否作为参照帧)。可以被参照的最小ref数是1。 -
bframes:在I帧与P帧之间可插入B帧数量(Number of B-frames)的最大值,范围0-16。 -
deblock:控制循环筛选(亦称为持续循环去区块(inloop deblocker))。 -
psy-rd:第一个数是Psy-RDO的强度(需要subme>=6)。第二个数是Psy-Trellis的强度(需要trellis>=1)。 -
aq-strength:弹性量化强度。设定AQ偏向低细节(平面)的宏区块之强度。不允许为负数。0.0~2.0以外的值不建议。 -
no-dct-decimate:停用DCT Decimation。DCT Decimation会舍弃它认为“不必要的”DCT区块。这会改善编码效率,而降低的品质通常微不足道。 -
deadzone-inter/intra:设定inter/intra亮度量化反应区(deadzone)的大小。反应区的范围应该在0~32。此值设定x264会任意舍弃而不尝试保留细微细节的层级。非常细微的细节既难以看见又耗费位元数,舍弃这些细节可以不用浪费位元数在视讯的此类低收益画面上。反应区与–trellis不相容。 -
ipratio:修改I帧量化值相比P帧量化值的目标平均增量。越大的值会提高I帧的品质。 -
pbratio:修改B帧量化值相比P帧量化值的目标平均减量。越大的值会降低B帧的品质。当mbtree启用时(默认启用),此设定无作用,mbtree会自动计算最佳值。 -
qcomp:量化值曲线压缩系数。0.0是固定位元率,1.0则是固定量化值。当mbtree启用时,它会影响mbtree的强度(qcomp越大,mbtree越弱)。 -
aq-mode:弹性量化模式。没有AQ时,x264很容易分配不足的位元数到细节较少的部分。AQ是用来更好地分配视讯里所有宏区块之间的可用位元数。 -
no-cabac:停用弹性内容的二进制算数编码(CABAC:Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coder)资料流压缩,切换回效率较低的弹性内容的可变长度编码(CAVLC:Context Adaptive Variable Length Coder)系统。大幅降低压缩效率(通常10~20%)和解码的硬件需求。 -
weightp:使x264能够使用明确加权预测(explicit weighted prediction)来改善P帧的压缩。亦改善淡入/淡出的品质。模式越高越慢。 -
force-cfr:如果使用 ffms2 或 lavf 分离器,且输出文件不是 raw 格式,则从输入文件复制时间码。此选项关闭这个功能,并强制 x264 自己产生。当使用此选项时估计你也会设置 –fps。 -
no-mbtree:停用宏区块树(macroblock tree)位元率控制。使用宏区块树位元率控制会改善整体压缩率,借由追踪跨帧的时间传播(temporal propagation)并相应地加权。 -
sync-lookahead:设置用于线程预测的帧缓存大小。最大值是250。在第二遍及更多遍编码或基于分片线程时自动关闭。设为0将关闭线程预测,将减小延迟,但是以降低性能为代价。 -
sliced-threads:开启基于分片的线程。比默认方式质量低、效率低,但是没有编码延迟。 -
rc-lookahead:设定mb-tree位元率控制和vbv-lookahead使用的帧数。最大允许值是250。对于mb-tree部分,增加帧数带来更好的效果但也会更慢。mb-tree使用的最大缓冲值是MIN(rc-lookahead, –keyint)。
API 使用和解析
參考鏈接: 源碼地址;x264编码demo;
x264簡單使用代碼
// x264t.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdint.h"
#ifndef _DEBUG
#pragma comment(lib, "libx264.lib")//加載lib
#else
#pragma comment(lib, "libx264d.lib")//加載lib
#endif
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
//加入頭文件
#include "x264.h"
typedef char bool;
#define false 0;
#define true 1;
//编码图片帧
bool x264_encode_frame( x264_t *h,//x264解码原型对象,x264_t是一个控制X264编码的全局性结构体,该结构体控制着视频一帧一帧的编码,包括中间参考帧管理、码率控制、全局参数等一些重要参数和结构体。详见源码:https://code.videolan.org/videolan/x264/blob/master/common/common.h
x264_param_t *param,//结构体参数
x264_picture_t* pic_in,//输入图片
uint8_t* data_out,//数据输出
int* data_out_len,//输出长度
bool* key_frame);//是否为关键帧
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//获取输入参数
char *in_file = argv[1];//输入文件
char *out_file = argv[2];//输出文件
FILE *fp_in;//输入文件句柄
FILE *fp_out;//输出文件句柄
//预设相关参数
int width, //图片宽度
height, //图片高度
frame_size,//帧大小
plane0_size,//0通道大小
plane1_size,//1通道大小
plane2_size;//2通道大小
x264_param_t param;//设置x264参数
x264_t *h;//x264关键结构体
x264_picture_t pic;//输入图片
uint8_t *buffer;//缓冲
int actual_read_size;//读取到的大小
bool key_frame;//是否为,关键帧,
//存在多余参数
if(argc >= 5)
{
//获取输出宽高
sscanf(argv[3],"%dx%d",&width,&height);
//设置各个通道大小
plane0_size = plane1_size = plane2_size = height*width;
//判断YUV编码类型和方法:
//4\:4\:4表示完全取样。
//4\:2\:2表示2:1的水平取样,垂直完全采样。
//4\:2\:0表示2:1的水平取样,垂直2:1采样。
//4\:1\:1表示4:1的水平取样,垂直完全采样。
if(strcmp(argv[4],"444") == 0)
{
param.i_csp = X264_CSP_I444;//设置采样参数
//为图片分配内存大小
x264_picture_alloc( &pic, X264_CSP_I444, width, height);
}
else if(strcmp(argv[4],"422") == 0)
{
param.i_csp = X264_CSP_I422;
//垂直采样取半
plane1_size = plane2_size = plane0_size/2;
x264_picture_alloc( &pic, X264_CSP_I422, width, height );
}
else /*if(strcmp(argv[4],"420") == 0)*/
{
param.i_csp = X264_CSP_I420;
plane1_size = plane2_size = plane0_size/4;
x264_picture_alloc( &pic, X264_CSP_I420, width, height );
}
//确定帧大小=通道1size+通道2size+通道3size
frame_size = plane0_size + plane1_size + plane2_size;
//分配缓存
buffer = (uint8_t*)malloc(frame_size);
//设置默认参数
x264_param_default(param);
//设置编码参数
param.i_threads = 8;
param.i_width = width;
param.i_height = height;
param.i_bframe=3;
param.i_frame_reference=3;
param.rc.i_rc_method=X264_RC_CQP ;
param.i_csp = X264_CSP_I420;
param.b_visualize=1;
param.i_log_level=X264_LOG_NONE;
param.pf_log = printf;
//初始化文件和编码器
if( ( h = x264_encoder_open(param ) ) == NULL )
{
return -1;
}
if((fp_in =fopen(in_file,"rb")) == NULL)
{
puts("打开输入文件失败");
return -1;
}
if((fp_out =fopen(out_file,"wb")) == NULL)
{
puts("打开输出文件失败");
return -1;
}
do
{
//读取视频文件帧大小
actual_read_size = fread(buffer,frame_size,1,fp_in);
//读取到1帧则开始编码
if(actual_read_size == 1)
{
actual_read_size= frame_size;
//拷贝图像
memcpy(pic.img.plane[0], buffer, plane0_size);
memcpy(pic.img.plane[1], buffer + plane0_size, plane1_size);
memcpy(pic.img.plane[2], buffer + plane0_size + plane1_size, plane2_size);
pic.i_pts = (int64_t)param.i_frame_total * param.i_fps_den;
//编码
x264_encode_frame(h,param,&pic,buffer,&actual_read_size,&key_frame);
fwrite(buffer,actual_read_size,1,fp_out);
flushall();
}
else
{
fseek( fp_in, 0, SEEK_SET );
}
//帧数加一
param.i_frame_total ++;
}while(1);
//清除图片
x264_picture_clean( &pic );
//关闭解码器
x264_encoder_close( h );
//清除缓存
free(buffer);
//关闭文件
fclose(fp_out);
fclose(fp_in);
}
else
{
printf("%s","参数错误!");
}
return 0;
}
bool x264_encode_frame(x264_t *h, x264_param_t *param, x264_picture_t* pic_in, uint8_t* data_out,int* data_out_len, bool* key_frame )
{
x264_picture_t pic_out;//结构体描述一视频帧的特征,该结构体定义在x264.h中。
x264_nal_t *nal;//264_nal_t中的数据在下一次调用x264_encoder_encode之后就无效了,因此必须在调用x264_encoder_encode 或 x264_encoder_headers 之前使用或拷贝其中的数据。记录编码后获得的NAL单元个数
int i_nal,i;//nal单元首地址和辅助遍历
int i_size = 0;//每个NAL单元长度
int data_out_l = *data_out_len;//剩余长度
*data_out_len = 0;
//开始解码
if( x264_encoder_encode( h, &nal, &i_nal, pic_in, &pic_out ) < 0 )
{
return false;
}
for(i = 0; i < i_nal; i++ )
{
i_size = 0;
if( ( i_size = x264_nal_encode( data_out + *data_out_len, &data_out_l, 1, &nal[i] ) ) > 0 )
{
*data_out_len += i_size;
data_out_l -= i_size;
}
}
if(pic_out.i_type==X264_TYPE_IDR)
*key_frame = true;
return true;
}
x264函数功能总结
参考链接: X264函数功能总结;x264头文件结构体详解;FFmpeg实时解码H264;
| 函数名称 | 位置 | 完成功能 |
|---|---|---|
void x264_frame_filter |
common\mc.c |
帧滤波 |
void x264_frame_init_lowres |
common\mc.c |
亮度1/2像素值初始化 |
void x264_mc_init |
common\mc.c |
运动估计初始化 |
static void motion_compensation_chroma |
common\mc.c |
色度运动估计 |
static uint8_t *get_ref |
common\mc.c |
获取参考亮度像素 |
static void mc_luma |
common\mc.c |
亮度运动估计 |
void x264_param_default |
common\common.c |
设置缺省参数 |
void x264_log |
common\common.c |
定义log级别 |
static void x264_log_default |
common\common.c |
设置缺省日志参数 |
void x264_picture_alloc |
common\common.c |
设置picture参数,根据输出图像格式分配空间 |
void x264_picture_clean |
common\common.c |
释放分配的图像空间 |
int x264_nal_encode |
common\common.c |
nal单元编码 |
int x264_nal_decode |
common\common.c |
nal单元解码 |
void *x264_malloc |
common\common.c |
X264内部定义的内存分配 |
void x264_free |
common\common.c |
X264内存释放 |
void *x264_realloc |
common\common.c |
X264重新分配图像空间 |
void x264_reduce_fraction |
common\common.c |
分数化简 |
char *x264_slurp_file |
common\common.c |
将文件读入分配的缓存区 |
char *x264_param2string |
common\common.c |
转换参数为字符串,返回字符串存放的地址 |
void x264_cabac_context_init |
common\cabac.c |
CABAC上下文取值表初始化 |
void x264_cabac_decode_init |
common\cabac.c |
CABAC解码流初始化 |
static inline void x264_cabac_decode_renorm |
common\cabac.c |
CABAC解码重新标准化 |
int x264_cabac_decode_decision |
common\cabac.c |
|
int x264_cabac_decode_bypass |
common\cabac.c |
|
int x264_cabac_decode_terminal |
common\cabac.c |
|
void x264_cabac_encode_init |
common\cabac.c |
|
static inline void x264_cabac_putbit |
common\cabac.c |
|
static inline void x264_cabac_encode_renorm |
common\cabac.c |
|
void x264_cabac_encode_decision |
common\cabac.c |
|
void x264_cabac_encode_bypass |
common\cabac.c |
|
void x264_cabac_encode_terminal |
common\cabac.c |
|
void x264_cabac_encode_flush |
common\cabac.c |
|
void x264_cabac_size_decision |
common\cabac.c |
|
int x264_cabac_size_decision2 |
common\cabac.c |
|
int 264_cabac_size_decision_noup |
common\cabac.c |
|
static inline int clip_uint8 |
common\dct.c |
clip3(x,0,255) |
static void dct2x2dc |
common\dct.c |
22直流系数的Hadamard变换,以44变换为基础 |
static void dct4x4dc |
common\dct.c |
4*4DC系数的Hadamard变换 |
static void idct4x4dc |
common\dct.c |
每行每列一维蝶形快速算法,完成d[4][4]的Hadamard反变换 |
static void sub4x4_dct |
common\dct.c |
对4*4残差进行DCT变换 |
static void sub8x8_dct |
common\dct.c |
对8*8残差进行DCT变换 |
static void sub16x16_dct |
common\dct.c |
对16*16残差进行DCT变换 |
static void add4x4_idct |
common\dct.c |
残差块DCT反变换后,加到预测块上,重构4*4块 |
static void add8x8_idct |
common\dct.c |
残差块DCT反变换后,加到预测块上,重构8*8块 |
static void add16x16_idct |
common\dct.c |
残差块DCT反变换后,加到预测块上,重构16*16块 |
void x264_dct_init |
common\dct.c |
DCT运算初始化 |
static void quant_8x8_core |
common\quant.c |
8*8 AC量化 |
static void quant_4x4_core |
common\quant.c |
4*4 AC量化 |
static void quant_4x4_dc_core |
common\quant.c |
4*4 亮度DC量化 |
static void quant_2x2_dc_core |
common\quant.c |
2*2 色度DC量化 |
static void dequant_4x4 |
common\quant.c |
4*4 AC反量化 |
static void dequant_8x8 |
common\quant.c |
8*8 AC反量化 |
void x264_mb_dequant_2x2_dc |
common\quant.c |
2*2 色度DC反量化 |
void x264_mb_dequant_4x4_dc |
common\quant.c |
4*4 亮度DC反量化 |
void x264_quant_init |
common\quant.c |
量化参量初始化 |
x264_frame_t *x264_frame_new |
common\frame.c |
创建新帧 |
void x264_frame_delete |
common\frame.c |
删除帧,释放空间 |
void x264_frame_copy_picture |
common\frame.c |
将图像拷贝到帧中 |
static void plane_expand_border |
common\frame.c |
边界扩展(被其他具体的扩展函数调用) |
void x264_frame_expand_border |
common\frame.c |
帧边界扩展 |
void x264_frame_expand_border_filtered |
common\frame.c |
为滤波进行的边界扩展 |
void x264_frame_expand_border_lowres |
common\frame.c |
为计算亮度半像素值进行边界扩展 |
void x264_frame_expand_border_mod16 |
common\frame.c |
帧边界不是16整数倍时进行边界扩展 |
static inline void deblock_luma_c |
common\frame.c |
bs=1~3时,修正亮度MB边界的p0和q0值 |
static void deblock_v_luma_c |
common\frame.c |
亮度分量垂直边界去块滤波 |
static void deblock_h_luma_c |
common\frame.c |
亮度分量水平边界去块滤波 |
static inline void deblock_chroma_c |
common\frame.c |
bs=1~3时,修正色度MB边界的p0和q0值 |
static void deblock_v_chroma_c |
common\frame.c |
色度分量垂直边界去块滤波 |
static void deblock_h_chroma_c |
common\frame.c |
色度分量水平边界去块滤波 |
static inline void deblock_luma_intra_c |
common\frame.c |
bs=4时,修正亮度MB边界的值 |
static void deblock_v_luma_intra_c |
common\frame.c |
帧内亮度分量垂直边界去块滤波 |
static void deblock_h_luma_intra_c |
common\frame.c |
帧内亮度分量水平边界去块滤波 |
static inline void deblock_chroma_intra_c |
common\frame.c |
bs=4时,修正色度MB边界的值 |
static void deblock_v_chroma_intra_c |
common\frame.c |
帧内色度分量垂直边界去块滤波 |
static void deblock_h_chroma_intra_c |
common\frame.c |
帧内色度分量水平边界去块滤波 |
static inline void deblock_edge |
common\frame.c |
bs值确定 |
void x264_frame_deblocking_filter |
common\frame.c |
帧去块滤波主函数 |
void x264_deblock_init |
common\frame.c |
去块滤波初始化 |
int x264_mb_predict_intra4x4_mode |
common\macroblock.c |
帧内4*4块模式预测 |
int x264_mb_predict_non_zero_code |
common\macroblock.c |
非零 |
int x264_mb_transform_8x8_allowed |
common\macroblock.c |
判断当前宏块是否允许8*8变换 |
void x264_mb_predict_mv |
common\macroblock.c |
宏块运动矢量预测 |
void x264_mb_predict_mv_16x16 |
common\macroblock.c |
16*16块MV预测 |
void x264_mb_predict_mv_pskip |
common\macroblock.c |
Pskip块MV预测 |
static int x264_mb_predict_mv_direct16x16_temporal |
common\macroblock.c |
直接模式16*16块MV时间预测 |
static int x264_mb_predict_mv_direct16x16_spatial |
common\macroblock.c |
直接模式16*16块MV空间预测 |
int x264_mb_predict_mv_direct16x16 |
common\macroblock.c |
直接模式16*16块MV预测 |
void x264_mb_load_mv_direct8x8 |
common\macroblock.c |
直接模式8*8块MV加载 |
void x264_mb_predict_mv_ref16x16 |
common\macroblock.c |
16*16参考块MV预测 |
static inline void x264_mb_mc_0xywh |
common\macroblock.c |
前向宏块运动补偿 |
static inline void x264_mb_mc_1xywh |
common\macroblock.c |
后向宏块运动补偿 |
static inline void x264_mb_mc_01xywh |
common\macroblock.c |
宏块双向运动补偿 |
static void x264_mb_mc_direct8x8 |
common\macroblock.c |
直接模式8*8块运动补偿 |
void x264_mb_mc_8x8 |
common\macroblock.c |
各种类型8*8块及其分割的运动补偿 |
void x264_mb_mc |
common\macroblock.c |
各种类型块运动补偿(调用以上各MC子函数) |
void x264_macroblock_cache_init |
common\macroblock.c |
初始化表征宏块的各变量,分配内存空间 |
void x264_macroblock_cache_end |
common\macroblock.c |
释放为宏块分配的cache空间 |
void x264_macroblock_slice_init |
common\macroblock.c |
初始MB与slice映射关系 |
void x264_macroblock_cache_load |
common\macroblock.c |
宏块cache加载,所有宏块表征变量赋值 |
void x264_macroblock_cache_save |
common\macroblock.c |
保存cache中的变量值 |
void x264_macroblock_bipred_init |
common\macroblock.c |
宏块双向预测初始化 |
int64_t x264_pixel_ssd_wxh |
common\pixel.c |
计算像素差值平方和 |
static inline void pixel_sub_wxh |
common\pixel.c |
计算像素差 |
static int pixel_satd_wxh |
common\pixel.c |
计算4*4hardmard变换后的绝对误差和 |
static inline int pixel_sa8d_wxh |
common\pixel.c |
计算8*8hardmard变换后的绝对误差和 |
static void predict_16x16_dc |
common\predict.c |
上和左邻块可用时,帧内16*16亮度块DC模式预测 |
static void predict_16x16_dc_left |
common\predict.c |
左边邻块可用时,帧内16*16亮度块DC模式预测 |
static void predict_16x16_dc_top |
common\predict.c |
上边邻块可用时,帧内16*16亮度块DC模式预测 |
static void predict_16x16_dc_128 |
common\predict.c |
邻块均不可用时,帧内16*16亮度块预测DC模式,预测值为128 |
static void predict_16x16_h |
common\predict.c |
帧内16*16亮度块水平预测 |
static void predict_16x16_v |
common\predict.c |
帧内16*16亮度块垂直预测 |
static void predict_16x16_p |
common\predict.c |
帧内16*16亮度块平面预测 |
static void predict_8x8c_dc_128 |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_dc_left |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_dc_top |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_dc |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_h |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_v |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_p |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_4x4c_dc_128 |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_4x4c_dc_left |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_4x4c_dc_top |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_4x4c_dc |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_4x4c_h |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_4x4c_v |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_4x4c_p |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_4x4_ddl |
common\predict.c |
模式3 左下对角预测 |
static void predict_4x4_ddr |
common\predict.c |
模式4 右下对角预测 |
static void predict_4x4_vr |
common\predict.c |
模式5 垂直左下角 |
static void predict_4x4_hd |
common\predict.c |
模式6 水平斜下角 |
static void predict_4x4_vl |
common\predict.c |
模式7 垂直左下角 |
static void predict_4x4_hu |
common\predict.c |
模式8 水平斜上角 |
static void predict_8x8c_dc_128 |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_dc_left |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_dc_top |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_dc |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_h |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_v |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8c_p |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8_ddl |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8_ddr |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8_vr |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8_hd |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8_vl |
common\predict.c |
|
static void predict_8x8_hu |
common\predict.c |
|
void x264_predict_16x16_init |
common\predict.c |
帧内16*16亮度块预测模式初始化 |
void x264_predict_8x8c_init( int cpu, x264_predict8x8_t pf[7] ) |
common\predict.c |
帧内8*8亮度块预测模式初始化(7种模式) |
void x264_predict_8x8c_init( int cpu, x264_predict8x8_t pf[12] ) |
common\predict.c |
帧内8*8亮度块预测模式初始化(12种模式) |
void x264_predict_4x4_init |
common\predict.c |
帧内4*4亮度块预测模式初始化 |
void x264_cqm_init |
common\set.c |
量化矩阵初始化 |
int x264_cqm_parse_jmlist |
common\set.c |
分析量化矩阵列表的正确性 |
int x264_cqm_parse_file |
common\set.c |
分析量化矩阵文件的正确性 |
static inline void x264_cabac_encode_ue_bypass |
encoder\cabac.c |
无符号指标GOLOMB编码 |
static inline void x264_cabac_mb_type_intra |
encoder\cabac.c |
宏块帧内类型cabac编码 |
static void x264_cabac_mb_type |
encoder\cabac.c |
宏块类型cabac编码 |
static void x264_cabac_mb_intra4x4_pred_mode |
encoder\cabac.c |
4*4帧内亮度块预测模式cabac编码 |
static void x264_cabac_mb_intra_chroma_pred_mode |
encoder\cabac.c |
帧内色度块预测模式cabac编码 |
static void x264_cabac_mb_cbp_luma |
encoder\cabac.c |
宏块亮度cbp值cabac编码 |
static void x264_cabac_mb_cbp_chroma |
encoder\cabac.c |
宏块色度cbp值cabac编码 |
static void x264_cabac_mb_qp_delta |
encoder\cabac.c |
宏块增量量化参数cabac编码 |
void x264_cabac_mb_skip |
encoder\cabac.c |
可跳过宏块cabac编码 |
static inline void x264_cabac_mb_sub_p_partition |
encoder\cabac.c |
8*8子宏块分割cabac编码 |
static inline void x264_cabac_mb_sub_b_partition |
encoder\cabac.c |
B帧8*8子宏块各种分割cabac编码 |
static inline void x264_cabac_mb_transform_size |
encoder\cabac.c |
宏块变换块尺寸cabac编码 |
static inline void x264_cabac_mb_ref |
encoder\cabac.c |
参考宏块cabac编码 |
static inline void x264_cabac_mb_mvd_cpn |
encoder\cabac.c |
宏块的mvd进行cabac编码 |
static inline void x264_cabac_mb_mvd |
encoder\cabac.c |
计算并保存宏块mvd,调用上个函数对mvd进行cabac编码 |
static inline void x264_cabac_mb8x8_mvd |
encoder\cabac.c |
8*8宏块mvd的cabac编码 |
static int x264_cabac_mb_cbf_ctxidxinc |
encoder\cabac.c |
返回宏块左边和上边块非0像素的个数 |
static void block_residual_write_cabac |
encoder\cabac.c |
残差块cabac编码 |
void x264_macroblock_write_cabac |
encoder\cabac.c |
宏块cabac编码主函数(调用以上各子函数) |
定义RD时使用 |
encoder\cabac.c |
|
void x264_partition_size_cabac |
encoder\cabac.c |
宏块分割cabac编码主函数 |
static void x264_partition_i8x8_size_cabac |
encoder\cabac.c |
|
static void x264_partition_i4x4_size_cabac |
encoder\cabac.c |
|
static void block_residual_write_cavlc |
encoder\cavlc.c |
残差块cavlc编码 |
static void cavlc_qp_delta |
encoder\cavlc.c |
量化参数增量cavlc编码 |
static void cavlc_mb_mvd |
encoder\cavlc.c |
运动矢量差值cavlc编码 |
static void cavlc_mb8x8_mvd |
encoder\cavlc.c |
8*8子宏块运动矢量差值cavlc编码 |
static inline void x264_macroblock_luma_write_cavlc |
encoder\cavlc.c |
亮度宏块cavlc编码 |
void x264_macroblock_write_cavlc |
encoder\cavlc.c |
宏块cavlc编码主函数 |
#ifdef RDO_SKIP_BS时使用下列 |
encoder\cavlc.c |
|
int x264_partition_size_cavlc |
encoder\cavlc.c |
|
static int cavlc_intra4x4_pred_size |
encoder\cavlc.c |
|
static int x264_partition_i8x8_size_cavlc |
encoder\cavlc.c |
|
static int x264_partition_i4x4_size_cavlc |
encoder\cavlc.c |
|
static double pop |
encoder\eval.c |
出栈 |
static void push |
encoder\eval.c |
入栈 |
static int strmatch |
encoder\eval.c |
串匹配 |
static void evalPrimary |
encoder\eval.c |
一些常用计算 |
static void evalPow |
encoder\eval.c |
运算式分析或计算 |
static void evalFactor |
encoder\eval.c |
求幂运算 |
static void evalTerm |
encoder\eval.c |
|
static void evalExpression |
encoder\eval.c |
|
double x264_eval |
encoder\eval.c |
输入运算变量和运算符,功能调用运算表达式分析函数 |
void x264_me_search_ref |
encoder\me.c |
运动估计搜索 |
void x264_me_refine_qpel |
亚像素运动估计 | |
static void refine_subpel |
亚像素运动估计搜索 | |
int x264_me_refine_bidir |
双向运动估计 | |
void x264_me_refine_qpel_rd |
有率失真的亚像素运动估计 |
x264源码分析和总结
参考链接: x264源代码简单分析:概述;